Knot Resolver library¶
For users¶
The library as described provides basic services for name resolution, which should cover the usage, examples are in the resolve API documentation.
Tip
If you’re migrating from getaddrinfo(), see “synchronous” API, but the library offers iterative API as well to plug it into your event loop for example.
For developers¶
The resolution process starts with the functions in resolve.c, they are responsible for:
reacting to state machine state (i.e. calling consume layers if we have an answer ready)
interacting with the library user (i.e. asking caller for I/O, accepting queries)
fetching assets needed by layers (i.e. zone cut)
This is the driver. The driver is not meant to know “how” the query resolves, but rather “when” to execute “what”.
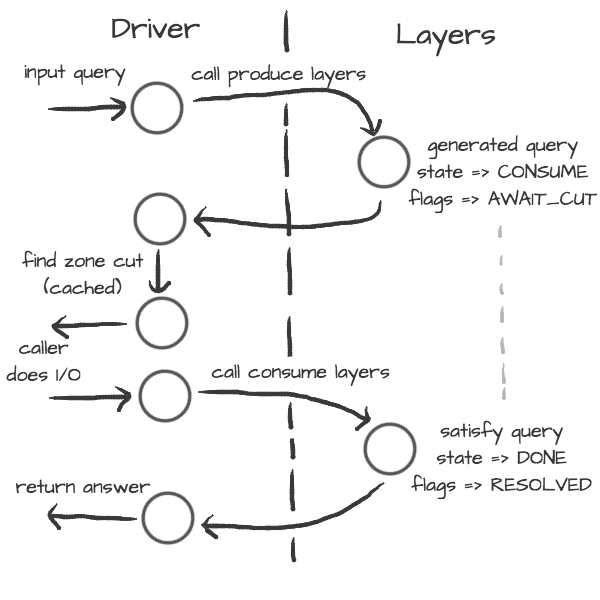
On the other side are layers. They are responsible for dissecting the packets and informing the driver about the results. For example, a produce layer generates query, a consume layer validates answer.
Tip
Layers are executed asynchronously by the driver. If you need some asset beforehand, you can signalize the driver using returning state or current query flags. For example, setting a flag AWAIT_CUT forces driver to fetch zone cut information before the packet is consumed; setting a RESOLVED flag makes it pop a query after the current set of layers is finished; returning FAIL state makes it fail current query.
Layers can also change course of resolution, for example by appending additional queries.
consume = function (state, req, answer)
if answer:qtype() == kres.type.NS then
local qry = req:push(answer:qname(), kres.type.SOA, kres.class.IN)
qry.flags.AWAIT_CUT = true
end
return state
end
This doesn’t block currently processed query, and the newly created sub-request will start as soon as driver finishes processing current. In some cases you might need to issue sub-request and process it before continuing with the current, i.e. validator may need a DNSKEY before it can validate signatures. In this case, layers can yield and resume afterwards.
consume = function (state, req, answer)
if state == kres.YIELD then
print('continuing yielded layer')
return kres.DONE
else
if answer:qtype() == kres.type.NS then
local qry = req:push(answer:qname(), kres.type.SOA, kres.class.IN)
qry.flags.AWAIT_CUT = true
print('planned SOA query, yielding')
return kres.YIELD
end
return state
end
end
The YIELD state is a bit special. When a layer returns it, it interrupts current walk through the layers. When the layer receives it,
it means that it yielded before and now it is resumed. This is useful in a situation where you need a sub-request to determine whether current answer is valid or not.
Writing layers¶
Warning
FIXME: this dev-docs section is outdated! Better see comments in files instead, for now.
The resolver library leverages the processing API from the libknot to separate packet processing code into layers.
Note
This is only crash-course in the library internals, see the resolver library documentation for the complete overview of the services.
The library offers following services:
Cache - MVCC cache interface for retrieving/storing resource records.
Resolution plan - Query resolution plan, a list of partial queries (with hierarchy) sent in order to satisfy original query. This contains information about the queries, nameserver choice, timing information, answer and its class.
Nameservers - Reputation database of nameservers, this serves as an aid for nameserver choice.
A processing layer is going to be called by the query resolution driver for each query, so you’re going to work with struct kr_request as your per-query context. This structure contains pointers to resolution context, resolution plan and also the final answer.
int consume(kr_layer_t *ctx, knot_pkt_t *pkt)
{
struct kr_request *req = ctx->req;
struct kr_query *qry = req->current_query;
}
This is only passive processing of the incoming answer. If you want to change the course of resolution, say satisfy a query from a local cache before the library issues a query to the nameserver, you can use states (see the Static hints for example).
int produce(kr_layer_t *ctx, knot_pkt_t *pkt)
{
struct kr_request *req = ctx->req;
struct kr_query *qry = req->current_query;
/* Query can be satisfied locally. */
if (can_satisfy(qry)) {
/* This flag makes the resolver move the query
* to the "resolved" list. */
qry->flags.RESOLVED = true;
return KR_STATE_DONE;
}
/* Pass-through. */
return ctx->state;
}
It is possible to not only act during the query resolution, but also to view the complete resolution plan afterwards. This is useful for analysis-type tasks, or “per answer” hooks.
int finish(kr_layer_t *ctx)
{
struct kr_request *req = ctx->req;
struct kr_rplan *rplan = req->rplan;
/* Print the query sequence with start time. */
char qname_str[KNOT_DNAME_MAXLEN];
struct kr_query *qry = NULL
WALK_LIST(qry, rplan->resolved) {
knot_dname_to_str(qname_str, qry->sname, sizeof(qname_str));
printf("%s at %u\n", qname_str, qry->timestamp);
}
return ctx->state;
}
APIs in Lua¶
The APIs in Lua world try to mirror the C APIs using LuaJIT FFI, with several differences and enhancements. There is not comprehensive guide on the API yet, but you can have a look at the bindings file.
Elementary types and constants¶
States are directly in
krestable, e.g.kres.YIELD, kres.CONSUME, kres.PRODUCE, kres.DONE, kres.FAIL.DNS classes are in
kres.classtable, e.g.kres.class.INfor Internet class.DNS types are in
kres.typetable, e.g.kres.type.AAAAfor AAAA type.DNS rcodes types are in
kres.rcodetable, e.g.kres.rcode.NOERROR.Packet sections (QUESTION, ANSWER, AUTHORITY, ADDITIONAL) are in the
kres.sectiontable.
Working with domain names¶
The internal API usually works with domain names in label format, you can convert between text and wire freely.
local dname = kres.str2dname('business.se')
local strname = kres.dname2str(dname)
Working with resource records¶
Resource records are stored as tables.
local rr = { owner = kres.str2dname('owner'),
ttl = 0,
class = kres.class.IN,
type = kres.type.CNAME,
rdata = kres.str2dname('someplace') }
print(kres.rr2str(rr))
RRSets in packet can be accessed using FFI, you can easily fetch single records.
local rrset = { ... }
local rr = rrset:get(0) -- Return first RR
print(kres.dname2str(rr:owner()))
print(rr:ttl())
print(kres.rr2str(rr))
Working with packets¶
Packet is the data structure that you’re going to see in layers very often. They consists of a header, and four sections: QUESTION, ANSWER, AUTHORITY, ADDITIONAL. The first section is special, as it contains the query name, type, and class; the rest of the sections contain RRSets.
First you need to convert it to a type known to FFI and check basic properties. Let’s start with a snippet of a consume layer.
consume = function (state, req, pkt)
print('rcode:', pkt:rcode())
print('query:', kres.dname2str(pkt:qname()), pkt:qclass(), pkt:qtype())
if pkt:rcode() ~= kres.rcode.NOERROR then
print('error response')
end
end
You can enumerate records in the sections.
local records = pkt:section(kres.section.ANSWER)
for i = 1, #records do
local rr = records[i]
if rr.type == kres.type.AAAA then
print(kres.rr2str(rr))
end
end
During produce or begin, you might want to want to write to packet. Keep in mind that you have to write packet sections in sequence, e.g. you can’t write to ANSWER after writing AUTHORITY, it’s like stages where you can’t go back.
pkt:rcode(kres.rcode.NXDOMAIN)
-- Clear answer and write QUESTION
pkt:recycle()
pkt:question('\7blocked', kres.class.IN, kres.type.SOA)
-- Start writing data
pkt:begin(kres.section.ANSWER)
-- Nothing in answer
pkt:begin(kres.section.AUTHORITY)
local soa = { owner = '\7blocked', ttl = 900, class = kres.class.IN, type = kres.type.SOA, rdata = '...' }
pkt:put(soa.owner, soa.ttl, soa.class, soa.type, soa.rdata)
Working with requests¶
The request holds information about currently processed query, enabled options, cache, and other extra data. You primarily need to retrieve currently processed query.
consume = function (state, req, pkt)
print(req.options)
print(req.state)
-- Print information about current query
local current = req:current()
print(kres.dname2str(current.owner))
print(current.stype, current.sclass, current.id, current.flags)
end
In layers that either begin or finalize, you can walk the list of resolved queries.
local last = req:resolved()
print(last.stype)
As described in the layers, you can not only retrieve information about current query, but also push new ones or pop old ones.
-- Push new query
local qry = req:push(pkt:qname(), kres.type.SOA, kres.class.IN)
qry.flags.AWAIT_CUT = true
-- Pop the query, this will erase it from resolution plan
req:pop(qry)
Significant Lua API changes¶
Incompatible changes since 3.0.0¶
In the main kres.* lua binding, there was only change in struct knot_rrset_t:
constructor now accepts TTL as additional parameter (defaulting to zero)
add_rdata() doesn’t accept TTL anymore (and will throw an error if passed)
In case you used knot_* functions and structures bound to lua:
knot_dname_is_sub(a, b): knot_dname_in_bailiwick(a, b) > 0
knot_rdata_rdlen(): knot_rdataset_at().len
knot_rdata_data(): knot_rdataset_at().data
knot_rdata_array_size(): offsetof(struct knot_data_t, data) + knot_rdataset_at().len
struct knot_rdataset: field names were renamed to .count and .rdata
some functions got inlined from headers, but you can use their kr_* clones: kr_rrsig_sig_inception(), kr_rrsig_sig_expiration(), kr_rrsig_type_covered(). Note that these functions now accept knot_rdata_t* instead of a pair knot_rdataset_t* and size_t - you can use knot_rdataset_at() for that.
knot_rrset_add_rdata() doesn’t take TTL parameter anymore
knot_rrset_init_empty() was inlined, but in lua you can use the constructor
knot_rrset_ttl() was inlined, but in lua you can use :ttl() method instead
knot_pkt_qname(), _qtype(), _qclass(), _rr(), _section() were inlined, but in lua you can use methods instead, e.g. myPacket:qname()
knot_pkt_free() takes knot_pkt_t* instead of knot_pkt_t**, but from lua you probably didn’t want to use that; constructor ensures garbage collection.
API reference¶
Warning
This section is generated with doxygen and breathe. Due to their limitations, some symbols may be incorrectly described or missing entirely. For exhaustive and accurate reference, refer to the header files instead.
Name resolution¶
The API provides an API providing a “consumer-producer”-like interface to enable user to plug it into existing event loop or I/O code.
Example usage of the iterative API:
// Create request and its memory pool
struct kr_request req = {
.pool = {
.ctx = mp_new (4096),
.alloc = (mm_alloc_t) mp_alloc
}
};
// Setup and provide input query
int state = kr_resolve_begin(&req, ctx, final_answer);
state = kr_resolve_consume(&req, query);
// Generate answer
while (state == KR_STATE_PRODUCE) {
// Additional query generate, do the I/O and pass back answer
state = kr_resolve_produce(&req, &addr, &type, query);
while (state == KR_STATE_CONSUME) {
int ret = sendrecv(addr, proto, query, resp);
// If I/O fails, make "resp" empty
state = kr_resolve_consume(&request, addr, resp);
knot_pkt_clear(resp);
}
knot_pkt_clear(query);
}
// "state" is either DONE or FAIL
kr_resolve_finish(&request, state);
Defines
-
kr_request_selected(req)¶ Initializer for an array of *_selected.
Enums
-
enum
kr_rank¶ RRset rank - for cache and ranked_rr_*.
The rank meaning consists of one independent flag - KR_RANK_AUTH, and the rest have meaning of values where only one can hold at any time. You can use one of the enums as a safe initial value, optionally | KR_RANK_AUTH; otherwise it’s best to manipulate ranks via the kr_rank_* functions.
See also:
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2181#section-5.4.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4035#section-4.3- Note
The representation is complicated by restrictions on integer comparison:
AUTH must be > than !AUTH
AUTH INSECURE must be > than AUTH (because it attempted validation)
!AUTH SECURE must be > than AUTH (because it’s valid)
Values:
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_INITIAL= 0¶ Did not attempt to validate.
It’s assumed compulsory to validate (or prove insecure).
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_OMIT¶ Do not attempt to validate.
(And don’t consider it a validation failure.)
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_TRY¶ Attempt to validate, but failures are non-fatal.
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_INDET= 4¶ Unable to determine whether it should be secure.
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_BOGUS¶ Ought to be secure but isn’t.
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_MISMATCH¶
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_MISSING¶ No RRSIG found for that owner+type combination.
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_INSECURE= 8¶ Proven to be insecure, i.e.
we have a chain of trust from TAs that cryptographically denies the possibility of existence of a positive chain of trust from the TAs to the record.
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_AUTH= 16¶ Authoritative data flag; the chain of authority was “verified”.
Even if not set, only in-bailiwick stuff is acceptable, i.e. almost authoritative (example: mandatory glue and its NS RR).
-
enumerator
KR_RANK_SECURE= 32¶ Verified whole chain of trust from the closest TA.
Functions
-
bool
kr_rank_check(uint8_t rank)¶ Check that a rank value is valid.
Meant for assertions.
-
bool
kr_rank_test(uint8_t rank, uint8_t kr_flag)¶ Test the presence of any flag/state in a rank, i.e.
including KR_RANK_AUTH.
-
void
kr_rank_set(uint8_t *rank, uint8_t kr_flag)¶ Set the rank state.
The _AUTH flag is kept as it was.
-
int
kr_resolve_begin(struct kr_request *request, struct kr_context *ctx, knot_pkt_t *answer)¶ Begin name resolution.
- Note
Expects a request to have an initialized mempool, the “answer” packet will be kept during the resolution and will contain the final answer at the end.
- Return
CONSUME (expecting query)
- Parameters
request: request state with initialized mempoolctx: resolution contextanswer: allocated packet for final answer
-
int
kr_resolve_consume(struct kr_request *request, const struct sockaddr *src, knot_pkt_t *packet)¶ Consume input packet (may be either first query or answer to query originated from kr_resolve_produce())
- Note
If the I/O fails, provide an empty or NULL packet, this will make iterator recognize nameserver failure.
- Return
any state
- Parameters
request: request state (awaiting input)src: [in] packet source addresspacket: [in] input packet
-
int
kr_resolve_produce(struct kr_request *request, struct sockaddr **dst, int *type, knot_pkt_t *packet)¶ Produce either next additional query or finish.
If the CONSUME is returned then dst, type and packet will be filled with appropriate values and caller is responsible to send them and receive answer. If it returns any other state, then content of the variables is undefined.
- Return
any state
- Parameters
request: request state (in PRODUCE state)dst: [out] possible address of the next nameservertype: [out] possible used socket type (SOCK_STREAM, SOCK_DGRAM)packet: [out] packet to be filled with additional query
-
int
kr_resolve_checkout(struct kr_request *request, const struct sockaddr *src, struct sockaddr *dst, int type, knot_pkt_t *packet)¶ Finalises the outbound query packet with the knowledge of the IP addresses.
- Note
The function must be called before actual sending of the request packet.
- Return
kr_ok() or error code
- Parameters
request: request state (in PRODUCE state)src: address from which the query is going to be sentdst: address of the name servertype: used socket type (SOCK_STREAM, SOCK_DGRAM)packet: [in,out] query packet to be finalised
-
int
kr_resolve_finish(struct kr_request *request, int state)¶ Finish resolution and commit results if the state is DONE.
- Note
The structures will be deinitialized, but the assigned memory pool is not going to be destroyed, as it’s owned by caller.
- Return
DONE
- Parameters
request: request statestate: either DONE or FAIL state (to be assigned to request->state)
-
struct kr_rplan *
kr_resolve_plan(struct kr_request *request)¶ Return resolution plan.
- Return
pointer to rplan
- Parameters
request: request state
-
knot_mm_t *
kr_resolve_pool(struct kr_request *request)¶ Return memory pool associated with request.
- Return
mempool
- Parameters
request: request state
-
struct
kr_context¶ - #include <resolve.h>
Name resolution context.
Resolution context provides basic services like cache, configuration and options.
- Note
This structure is persistent between name resolutions and may be shared between threads.
Public Members
-
knot_rrset_t *
opt_rr¶ Default EDNS towards both clients and upstream.
LATER: consider splitting the two, e.g. allow separately configured limits for UDP packet size (say, LAN is under control).
-
struct kr_zonecut
root_hints¶
-
kr_nsrep_rtt_lru_t *
cache_rtt¶
-
unsigned
cache_rtt_tout_retry_interval¶
-
kr_nsrep_lru_t *
cache_rep¶
-
module_array_t *
modules¶
-
int32_t
tls_padding¶ See net.tls_padding in ../daemon/README.rst -1 is “true” (default policy), 0 is “false” (no padding)
-
knot_mm_t *
pool¶
-
struct
kr_request_qsource_flags¶
-
struct
kr_request¶ - #include <resolve.h>
Name resolution request.
Keeps information about current query processing between calls to processing APIs, i.e. current resolved query, resolution plan, … Use this instead of the simple interface if you want to implement multiplexing or custom I/O.
- Note
All data for this request must be allocated from the given pool.
Public Members
-
struct kr_context *
ctx¶
-
knot_pkt_t *
answer¶
-
const struct sockaddr *
addr¶ Address that originated the request.
Current upstream address.
NULL for internal origin.
-
const struct sockaddr *
dst_addr¶ Address that accepted the request.
NULL for internal origin. Beware: in case of UDP on wildcard address it will be wildcard; closely related: issue #173.
-
const knot_pkt_t *
packet¶
-
struct kr_request_qsource_flags
flags¶ See definition above.
-
size_t
size¶ query packet size
-
struct kr_request::@6 qsource
-
unsigned
rtt¶ Current upstream RTT.
-
struct kr_request::@7 upstream Upstream information, valid only in consume() phase.
-
int
state¶
-
ranked_rr_array_t
answ_selected¶
-
ranked_rr_array_t
auth_selected¶
-
ranked_rr_array_t
add_selected¶
-
bool
answ_validated¶ internal to validator; beware of caching, etc.
-
bool
auth_validated¶ see answ_validated ^^ ; TODO
-
uint8_t
rank¶ Overall rank for the request.
Values from kr_rank, currently just KR_RANK_SECURE and _INITIAL. Only read this in finish phase and after validator, please. Meaning of _SECURE: all RRs in answer+authority are _SECURE, including any negative results implied (NXDOMAIN, NODATA).
-
trace_log_f
trace_log¶ Logging tracepoint.
-
trace_callback_f
trace_finish¶ Request finish tracepoint.
-
int
vars_ref¶ Reference to per-request variable table.
LUA_NOREF if not set.
-
knot_mm_t
pool¶
-
unsigned int
uid¶
-
unsigned int
count_no_nsaddr¶ for logging purposes only
-
unsigned int
count_fail_row¶
Typedefs
Functions
-
void
kr_qflags_set(struct kr_qflags *fl1, struct kr_qflags fl2)¶ Combine flags together.
This means set union for simple flags.
-
void
kr_qflags_clear(struct kr_qflags *fl1, struct kr_qflags fl2)¶ Remove flags.
This means set-theoretic difference.
-
int
kr_rplan_init(struct kr_rplan *rplan, struct kr_request *request, knot_mm_t *pool)¶ Initialize resolution plan (empty).
- Parameters
rplan: plan instancerequest: resolution requestpool: ephemeral memory pool for whole resolution
-
void
kr_rplan_deinit(struct kr_rplan *rplan)¶ Deinitialize resolution plan, aborting any uncommited transactions.
- Parameters
rplan: plan instance
-
bool
kr_rplan_empty(struct kr_rplan *rplan)¶ Return true if the resolution plan is empty (i.e.
finished or initialized)
- Return
true or false
- Parameters
rplan: plan instance
-
struct kr_query *
kr_rplan_push_empty(struct kr_rplan *rplan, struct kr_query *parent)¶ Push empty query to the top of the resolution plan.
- Note
This query serves as a cookie query only.
- Return
query instance or NULL
- Parameters
rplan: plan instanceparent: query parent (or NULL)
-
struct kr_query *
kr_rplan_push(struct kr_rplan *rplan, struct kr_query *parent, const knot_dname_t *name, uint16_t cls, uint16_t type)¶ Push a query to the top of the resolution plan.
- Note
This means that this query takes precedence before all pending queries.
- Return
query instance or NULL
- Parameters
rplan: plan instanceparent: query parent (or NULL)name: resolved namecls: resolved classtype: resolved type
-
int
kr_rplan_pop(struct kr_rplan *rplan, struct kr_query *qry)¶ Pop existing query from the resolution plan.
- Note
Popped queries are not discarded, but moved to the resolved list.
- Return
0 or an error
- Parameters
rplan: plan instanceqry: resolved query
-
bool
kr_rplan_satisfies(struct kr_query *closure, const knot_dname_t *name, uint16_t cls, uint16_t type)¶ Return true if resolution chain satisfies given query.
-
struct kr_query *
kr_rplan_last(struct kr_rplan *rplan)¶ Return last query (either currently being solved or last resolved).
This is necessary to retrieve the last query in case of resolution failures (e.g. time limit reached).
-
struct kr_query *
kr_rplan_find_resolved(struct kr_rplan *rplan, struct kr_query *parent, const knot_dname_t *name, uint16_t cls, uint16_t type)¶ Check if a given query already resolved.
- Return
query instance or NULL
- Parameters
rplan: plan instanceparent: query parent (or NULL)name: resolved namecls: resolved classtype: resolved type
-
struct
kr_qflags¶ - #include <rplan.h>
Query flags.
Public Members
-
bool
NO_MINIMIZE¶ Don’t minimize QNAME.
-
bool
NO_THROTTLE¶ No query/slow NS throttling.
-
bool
NO_IPV6¶ Disable IPv6.
-
bool
NO_IPV4¶ Disable IPv4.
-
bool
TCP¶ Use TCP for this query.
-
bool
RESOLVED¶ Query is resolved.
Note that kr_query gets RESOLVED before following a CNAME chain; see .CNAME.
-
bool
AWAIT_IPV4¶ Query is waiting for A address.
-
bool
AWAIT_IPV6¶ Query is waiting for AAAA address.
-
bool
AWAIT_CUT¶ Query is waiting for zone cut lookup.
-
bool
SAFEMODE¶ Don’t use fancy stuff (EDNS, 0x20, …)
-
bool
CACHED¶ Query response is cached.
-
bool
NO_CACHE¶ No cache for lookup; exception: finding NSs and subqueries.
-
bool
EXPIRING¶ Query response is cached, but expiring.
-
bool
ALLOW_LOCAL¶ Allow queries to local or private address ranges.
-
bool
DNSSEC_WANT¶ Want DNSSEC secured answer; exception: +cd, i.e.
knot_wire_set_cd(request->answer->wire).
-
bool
DNSSEC_BOGUS¶ Query response is DNSSEC bogus.
-
bool
DNSSEC_INSECURE¶ Query response is DNSSEC insecure.
-
bool
DNSSEC_CD¶ Instruction to set CD bit in request.
-
bool
STUB¶ Stub resolution, accept received answer as solved.
-
bool
ALWAYS_CUT¶ Always recover zone cut (even if cached).
-
bool
DNSSEC_WEXPAND¶ Query response has wildcard expansion.
-
bool
PERMISSIVE¶ Permissive resolver mode.
-
bool
STRICT¶ Strict resolver mode.
-
bool
BADCOOKIE_AGAIN¶ Query again because bad cookie returned.
-
bool
CNAME¶ Query response contains CNAME in answer section.
-
bool
REORDER_RR¶ Reorder cached RRs.
-
bool
TRACE¶ Also log answers if verbose.
-
bool
NO_0X20¶ Disable query case randomization .
-
bool
DNSSEC_NODS¶ DS non-existance is proven.
-
bool
DNSSEC_OPTOUT¶ Closest encloser proof has optout.
-
bool
NONAUTH¶ Non-authoritative in-bailiwick records are enough.
TODO: utilize this also outside cache.
-
bool
FORWARD¶ Forward all queries to upstream; validate answers.
-
bool
DNS64_MARK¶ Internal mark for dns64 module.
-
bool
CACHE_TRIED¶ Internal to cache module.
-
bool
NO_NS_FOUND¶ No valid NS found during last PRODUCE stage.
-
bool
PKT_IS_SANE¶ Set by iterator in consume phase to indicate whether some basic aspects of the packet are OK, e.g.
QNAME.
-
bool
-
struct
kr_query¶ - #include <rplan.h>
Single query representation.
Public Members
-
knot_dname_t *
sname¶ The name to resolve - lower-cased, uncompressed.
-
uint16_t
stype¶
-
uint16_t
sclass¶
-
uint16_t
id¶
-
uint16_t
reorder¶ Seed to reorder (cached) RRs in answer or zero.
-
uint32_t
secret¶
-
uint64_t
creation_time_mono¶
-
uint64_t
timestamp_mono¶ Time of query created or time of query to upstream resolver (milliseconds).
-
struct timeval
timestamp¶ Real time for TTL+DNSSEC checks (.tv_sec only).
-
struct kr_zonecut
zone_cut¶
-
struct kr_layer_pickle *
deferred¶
-
int8_t
cname_depth¶ Current xNAME depth, set by iterator.
0 = uninitialized, 1 = no CNAME, … See also KR_CNAME_CHAIN_LIMIT.
-
struct kr_query *
cname_parent¶ Pointer to the query that originated this one because of following a CNAME (or NULL).
-
struct kr_request *
request¶ Parent resolution request.
-
kr_stale_cb
stale_cb¶ See the type.
-
knot_dname_t *
-
struct
kr_rplan¶ - #include <rplan.h>
Query resolution plan structure.
The structure most importantly holds the original query, answer and the list of pending queries required to resolve the original query. It also keeps a notion of current zone cut.
Public Members
-
kr_qarray_t
pending¶ List of pending queries.
Beware: order is significant ATM, as the last is the next one to solve, and they may be inter-dependent.
-
kr_qarray_t
resolved¶ List of resolved queries.
-
struct kr_request *
request¶ Parent resolution request.
-
knot_mm_t *
pool¶ Temporary memory pool.
-
uint32_t
next_uid¶ Next value for kr_query::uid (incremental).
-
kr_qarray_t
Cache¶
Functions
-
int
cache_peek(kr_layer_t *ctx, knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶
-
int
cache_stash(kr_layer_t *ctx, knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶
-
int
kr_cache_open(struct kr_cache *cache, const struct kr_cdb_api *api, struct kr_cdb_opts *opts, knot_mm_t *mm)¶ Open/create cache with provided storage options.
- Return
0 or an error code
- Parameters
cache: cache structure to be initializedapi: storage engine APIopts: storage-specific options (may be NULL for default)mm: memory context.
-
void
kr_cache_close(struct kr_cache *cache)¶ Close persistent cache.
- Note
This doesn’t clear the data, just closes the connection to the database.
- Parameters
cache: structure
-
int
kr_cache_commit(struct kr_cache *cache)¶ Run after a row of operations to release transaction/lock if needed.
-
int
kr_cache_insert_rr(struct kr_cache *cache, const knot_rrset_t *rr, const knot_rrset_t *rrsig, uint8_t rank, uint32_t timestamp)¶ Insert RRSet into cache, replacing any existing data.
- Return
0 or an errcode
- Parameters
cache: cache structurerr: inserted RRSetrrsig: RRSIG for inserted RRSet (optional)rank: rank of the datatimestamp: current time
-
int
kr_cache_clear(struct kr_cache *cache)¶ Clear all items from the cache.
- Return
if nonzero is returned, there’s a big problem - you probably want to abort(), perhaps except for kr_error(EAGAIN) which probably indicates transient errors.
- Parameters
cache: cache structure
-
int
kr_cache_peek_exact(struct kr_cache *cache, const knot_dname_t *name, uint16_t type, struct kr_cache_p *peek)¶
-
int32_t
kr_cache_ttl(const struct kr_cache_p *peek, const struct kr_query *qry, const knot_dname_t *name, uint16_t type)¶
-
int
kr_cache_materialize(knot_rdataset_t *dst, const struct kr_cache_p *ref, knot_mm_t *pool)¶
-
int
kr_cache_remove(struct kr_cache *cache, const knot_dname_t *name, uint16_t type)¶ Remove an entry from cache.
- Return
number of deleted records, or negative error code
- Note
only “exact hits” are considered ATM, and some other information may be removed alongside.
- Parameters
cache: cache structurename: dnametype: rr type
-
int
kr_cache_match(struct kr_cache *cache, const knot_dname_t *name, bool exact_name, knot_db_val_t keyval[][2], int maxcount)¶ Get keys matching a dname lf prefix.
- Return
result count or an errcode
- Note
the cache keys are matched by prefix, i.e. it very much depends on their structure; CACHE_KEY_DEF.
- Parameters
cache: cache structurename: dnameexact_name: whether to only consider exact name matcheskeyval: matched key-value pairsmaxcount: limit on the number of returned key-value pairs
-
int
kr_cache_remove_subtree(struct kr_cache *cache, const knot_dname_t *name, bool exact_name, int maxcount)¶ Remove a subtree in cache.
It’s like _match but removing them instead of returning.
- Return
number of deleted entries or an errcode
-
int
kr_cache_closest_apex(struct kr_cache *cache, const knot_dname_t *name, bool is_DS, knot_dname_t **apex)¶ Find the closest cached zone apex for a name (in cache).
- Return
the number of labels to remove from the name, or negative error code
- Note
timestamp is found by a syscall, and stale-serving is not considered
- Parameters
is_DS: start searching one name higher
-
int
kr_unpack_cache_key(knot_db_val_t key, knot_dname_t *buf, uint16_t *type)¶ Unpack dname and type from db key.
- Return
length of dname or an errcode
- Note
only “exact hits” are considered ATM, moreover xNAME records are “hidden” as NS. (see comments in struct entry_h)
- Parameters
key: db key representationbuf: output buffer of domain name in dname formattype: output for type
Variables
-
const size_t
PKT_SIZE_NOWIRE= -1¶ When knot_pkt is passed from cache without ->wire, this is the ->size.
-
const char *
kr_cache_emergency_file_to_remove¶ Path to cache file to remove on critical out-of-space error.
(do NOT modify it)
-
struct
kr_cache¶ - #include <api.h>
Cache structure, keeps API, instance and metadata.
Public Members
-
knot_db_t *
db¶ Storage instance.
-
const struct kr_cdb_api *
api¶ Storage engine.
-
struct kr_cdb_stats
stats¶
-
uint32_t
ttl_min¶
-
uint32_t
ttl_max¶ TTL limits.
-
struct timeval
checkpoint_walltime¶ Wall time on the last check-point.
-
uint64_t
checkpoint_monotime¶ Monotonic milliseconds on the last check-point.
-
uv_timer_t *
health_timer¶ Timer used for kr_cache_check_health()
-
knot_db_t *
-
struct
kr_cache_p¶
Nameservers¶
Defines
-
KR_NS_DEAD¶ See kr_nsrep_update_rtt()
-
KR_NS_FWD_DEAD¶
-
KR_NS_TIMEOUT_RETRY_INTERVAL¶ If once NS was marked as “timeouted”, it won’t participate in NS elections at least KR_NS_TIMEOUT_RETRY_INTERVAL milliseconds (now: one second).
-
KR_NSREP_MAXADDR¶
Typedefs
-
typedef struct kr_nsrep_rtt_lru_entry
kr_nsrep_rtt_lru_entry_t¶
-
typedef see_source_code
kr_nsrep_rtt_lru_t¶ NS QoS tracking.
-
typedef see_source_code
kr_nsrep_lru_t¶ NS reputation tracking.
Enums
-
enum
kr_ns_score¶ NS RTT score (special values).
- Note
RTT is measured in milliseconds.
Values:
-
enumerator
KR_NS_MAX_SCORE= 20 * KR_CONN_RTT_MAX¶
-
enumerator
KR_NS_FWD_TIMEOUT= (95 * 10000) / 100¶
-
enumerator
KR_NS_TIMEOUT= (95 * KR_CONN_RTT_MAX) / 100¶
-
enumerator
KR_NS_LONG= (3 * KR_NS_TIMEOUT) / 4¶
-
enumerator
KR_NS_UNKNOWN= KR_NS_TIMEOUT / 2¶
-
enumerator
KR_NS_PENALTY= 100¶
-
enumerator
KR_NS_GLUED= 10¶
-
enum
kr_ns_rep¶ NS QoS flags.
Values:
-
enumerator
KR_NS_NOIP4= 1 << 0¶ NS has no IPv4.
-
enumerator
KR_NS_NOIP6= 1 << 1¶ NS has no IPv6.
-
enumerator
KR_NS_NOEDNS= 1 << 2¶ NS has no EDNS support.
-
enumerator
-
enum
kr_ns_update_mode¶ NS RTT update modes.
First update is always KR_NS_RESET unless KR_NS_UPDATE_NORESET mode had choosen.
Values:
-
enumerator
KR_NS_UPDATE= 0¶ Update as smooth over last two measurements.
-
enumerator
KR_NS_UPDATE_NORESET¶ Same as KR_NS_UPDATE, but disable fallback to KR_NS_RESET on newly added entries.
Zero is used as initial value.
-
enumerator
KR_NS_RESET¶ Set to given value.
-
enumerator
KR_NS_ADD¶ Increment current value.
-
enumerator
KR_NS_MAX¶ Set to maximum of current/proposed value.
-
enumerator
Functions
-
int
kr_nsrep_set(struct kr_query *qry, size_t index, const struct sockaddr *sock)¶ Set given NS address.
(Very low-level access to the list.)
- Return
0 or an error code, in particular kr_error(ENOENT) for net.ipvX
- Parameters
qry: updated queryindex: index of the updated targetsock: socket address to use (sockaddr_in or sockaddr_in6 or NULL)
-
int
kr_nsrep_elect(struct kr_query *qry, struct kr_context *ctx)¶ Elect best nameserver/address pair from the nsset.
- Return
0 or an error code
- Parameters
qry: updated queryctx: resolution context
-
int
kr_nsrep_elect_addr(struct kr_query *qry, struct kr_context *ctx)¶ Elect best nameserver/address pair from the nsset.
- Return
0 or an error code
- Parameters
qry: updated queryctx: resolution context
-
int
kr_nsrep_update_rtt(struct kr_nsrep *ns, const struct sockaddr *addr, unsigned score, kr_nsrep_rtt_lru_t *cache, int umode)¶ Update NS address RTT information.
In KR_NS_UPDATE mode reputation is smoothed over last N measurements.
- Return
0 on success, error code on failure
- Parameters
ns: updated NS representationaddr: chosen address (NULL for first)score: new score (i.e. RTT), see enum kr_ns_scorecache: RTT LRU cacheumode: update mode (KR_NS_UPDATE or KR_NS_RESET or KR_NS_ADD)
-
int
kr_nsrep_update_rep(struct kr_nsrep *ns, unsigned reputation, kr_nsrep_lru_t *cache)¶ Update NSSET reputation information.
- Return
0 on success, error code on failure
- Parameters
ns: updated NS representationreputation: combined reputation flags, see enum kr_ns_repcache: LRU cache
-
int
kr_nsrep_copy_set(struct kr_nsrep *dst, const struct kr_nsrep *src)¶ Copy NSSET reputation information and resets score.
- Return
0 on success, error code on failure
- Parameters
dst: updated NS representationsrc: source NS representation
-
int
kr_nsrep_sort(struct kr_nsrep *ns, struct kr_context *ctx)¶ Sort addresses in the query nsrep list by cached RTT.
if RTT is greater then KR_NS_TIMEOUT, address will placed at the beginning of the nsrep list once in cache.ns_tout() milliseconds. Otherwise it will be sorted as if it has cached RTT equal to KR_NS_MAX_SCORE + 1.
- Return
0 or an error code
- Note
ns reputation is zeroed and score is set to KR_NS_MAX_SCORE + 1.
- Parameters
ns: updated kr_nsrepctx: name resolution context.
-
struct
kr_nsrep_rtt_lru_entry¶
-
struct
kr_nsrep¶ - #include <nsrep.h>
Name server representation.
Contains extra information about the name server, e.g. score or other metadata.
Functions
-
int
kr_zonecut_init(struct kr_zonecut *cut, const knot_dname_t *name, knot_mm_t *pool)¶ Populate root zone cut with SBELT.
- Return
0 or error code
- Parameters
cut: zone cutname:pool:
-
void
kr_zonecut_deinit(struct kr_zonecut *cut)¶ Clear the structure and free the address set.
- Parameters
cut: zone cut
-
void
kr_zonecut_move(struct kr_zonecut *to, const struct kr_zonecut *from)¶ Move a zonecut, transferring ownership of any pointed-to memory.
- Parameters
to: the target - it gets deinit-edfrom: the source - not modified, but shouldn’t be used afterward
-
void
kr_zonecut_set(struct kr_zonecut *cut, const knot_dname_t *name)¶ Reset zone cut to given name and clear address list.
- Note
This clears the address list even if the name doesn’t change. TA and DNSKEY don’t change.
- Parameters
cut: zone cut to be setname: new zone cut name
-
int
kr_zonecut_copy(struct kr_zonecut *dst, const struct kr_zonecut *src)¶ Copy zone cut, including all data.
Does not copy keys and trust anchor.
- Return
0 or an error code; If it fails with kr_error(ENOMEM), it may be in a half-filled state, but it’s safe to deinit…
- Note
addresses for names in
srcget replaced and others are left as they were.- Parameters
dst: destination zone cutsrc: source zone cut
-
int
kr_zonecut_copy_trust(struct kr_zonecut *dst, const struct kr_zonecut *src)¶ Copy zone trust anchor and keys.
- Return
0 or an error code
- Parameters
dst: destination zone cutsrc: source zone cut
-
int
kr_zonecut_add(struct kr_zonecut *cut, const knot_dname_t *ns, const void *data, int len)¶ Add address record to the zone cut.
The record will be merged with existing data, it may be either A/AAAA type.
- Return
0 or error code
- Parameters
cut: zone cut to be populatedns: nameserver namedata: typically knot_rdata_t::datalen: typically knot_rdata_t::len
-
int
kr_zonecut_del(struct kr_zonecut *cut, const knot_dname_t *ns, const void *data, int len)¶ Delete nameserver/address pair from the zone cut.
- Return
0 or error code
- Parameters
cut:ns: name server namedata: typically knot_rdata_t::datalen: typically knot_rdata_t::len
-
int
kr_zonecut_del_all(struct kr_zonecut *cut, const knot_dname_t *ns)¶ Delete all addresses associated with the given name.
- Return
0 or error code
- Parameters
cut:ns: name server name
-
pack_t *
kr_zonecut_find(struct kr_zonecut *cut, const knot_dname_t *ns)¶ Find nameserver address list in the zone cut.
- Note
This can be used for membership test, a non-null pack is returned if the nameserver name exists.
- Return
pack of addresses or NULL
- Parameters
cut:ns: name server name
-
int
kr_zonecut_set_sbelt(struct kr_context *ctx, struct kr_zonecut *cut)¶ Populate zone cut with a root zone using SBELT :rfc:
1034- Return
0 or error code
- Parameters
ctx: resolution context (to fetch root hints)cut: zone cut to be populated
-
int
kr_zonecut_find_cached(struct kr_context *ctx, struct kr_zonecut *cut, const knot_dname_t *name, const struct kr_query *qry, bool *restrict secured)¶ Populate zone cut address set from cache.
- Return
0 or error code (ENOENT if it doesn’t find anything)
- Parameters
ctx: resolution context (to fetch data from LRU caches)cut: zone cut to be populatedname: QNAME to start finding zone cut forqry: query for timestamp and stale-serving decisionssecured: set to true if want secured zone cut, will return false if it is provably insecure
-
bool
kr_zonecut_is_empty(struct kr_zonecut *cut)¶ Check if any address is present in the zone cut.
- Return
true/false
- Parameters
cut: zone cut to check
-
struct
kr_zonecut¶ - #include <zonecut.h>
Current zone cut representation.
Modules¶
Module API definition and functions for (un)loading modules.
Defines
-
KR_MODULE_EXPORT(module)¶ Export module API version (place this at the end of your module).
- Parameters
module: module name (e.g. policy)
-
KR_MODULE_API¶
Functions
-
int
kr_module_load(struct kr_module *module, const char *name, const char *path)¶ Load a C module instance into memory.
And call its init().
- Return
0 or an error
- Parameters
module: module structure. Will be overwritten except for ->data on success.name: module namepath: module search path
-
void
kr_module_unload(struct kr_module *module)¶ Unload module instance.
- Note
currently used even for lua modules
- Parameters
module: module structure
-
kr_module_init_cb
kr_module_get_embedded(const char *name)¶ Get embedded module’s init function by name (or NULL).
-
struct
kr_module¶ - #include <module.h>
Module representation.
The five symbols (init, …) may be defined by the module as name_init(), etc; all are optional and missing symbols are represented as NULLs;
Public Members
-
char *
name¶
-
int (*
init)(struct kr_module *self)¶ Constructor.
Called after loading the module.
- Return
error code. Lua modules: not populated, called via lua directly.
-
int (*
deinit)(struct kr_module *self)¶ Destructor.
Called before unloading the module.
- Return
error code.
-
int (*
config)(struct kr_module *self, const char *input)¶ Configure with encoded JSON (NULL if missing).
- Return
error code. Lua modules: not used and not useful from C. When called from lua, input is JSON, like for kr_prop_cb.
-
const kr_layer_api_t *
layer¶ Packet processing API specs.
May be NULL. See docs on that type. Owned by the module code.
-
const struct kr_prop *
props¶ List of properties.
May be NULL. Terminated by { NULL, NULL, NULL }. Lua modules: not used and not useful.
-
void *
lib¶ dlopen() handle; RTLD_DEFAULT for embedded modules; NULL for lua modules.
-
void *
data¶ Custom data context.
-
char *
-
struct
kr_prop¶ - #include <module.h>
Module property (named callable).
Defines
Typedefs
-
typedef struct kr_layer_api
kr_layer_api_t¶
Enums
-
enum
kr_layer_state¶ Layer processing states.
Only one value at a time (but see TODO).
Each state represents the state machine transition, and determines readiness for the next action. See struct kr_layer_api for the actions.
TODO: the cookie module sometimes sets (_FAIL | _DONE) on purpose (!)
Values:
-
enumerator
KR_STATE_CONSUME= 1 << 0¶ Consume data.
-
enumerator
KR_STATE_PRODUCE= 1 << 1¶ Produce data.
-
enumerator
KR_STATE_DONE= 1 << 2¶ Finished successfully or a special case: in CONSUME phase this can be used (by iterator) to do a transition to PRODUCE phase again, in which case the packet wasn’t accepted for some reason.
-
enumerator
KR_STATE_FAIL= 1 << 3¶ Error.
-
enumerator
KR_STATE_YIELD= 1 << 4¶ Paused, waiting for a sub-query.
-
enumerator
Functions
-
bool
kr_state_consistent(enum kr_layer_state s)¶ Check that a kr_layer_state makes sense.
We’re not very strict ATM.
-
struct
kr_layer¶ - #include <layer.h>
Packet processing context.
Public Members
-
int
state¶ The current state; bitmap of enum kr_layer_state.
-
struct kr_request *
req¶ The corresponding request.
-
const struct kr_layer_api *
api¶
-
knot_pkt_t *
pkt¶ In glue for lua kr_layer_api it’s used to pass the parameter.
-
struct sockaddr *
dst¶ In glue for checkout layer it’s used to pass the parameter.
-
bool
is_stream¶ In glue for checkout layer it’s used to pass the parameter.
-
int
-
struct
kr_layer_api¶ - #include <layer.h>
Packet processing module API.
All functions return the new kr_layer_state.
Lua modules are allowed to return nil/nothing, meaning the state shall not change.
Public Members
-
int (*
begin)(kr_layer_t *ctx)¶ Start of processing the DNS request.
-
int (*
reset)(kr_layer_t *ctx)¶
-
int (*
finish)(kr_layer_t *ctx)¶ Paired to begin, called both on successes and failures.
-
int (*
consume)(kr_layer_t *ctx, knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶ Process an answer from upstream or from cache.
Lua API: call is omitted iff (state & KR_STATE_FAIL).
-
int (*
produce)(kr_layer_t *ctx, knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶ Produce either an answer to the request or a query for upstream (or fail).
Lua API: call is omitted iff (state & KR_STATE_FAIL).
-
int (*
checkout)(kr_layer_t *ctx, knot_pkt_t *packet, struct sockaddr *dst, int type)¶ Finalises the outbound query packet with the knowledge of the IP addresses.
The checkout layer doesn’t persist the state, so canceled subrequests don’t affect the resolution or rest of the processing. Lua API: call is omitted iff (state & KR_STATE_FAIL).
-
int (*
answer_finalize)(kr_layer_t *ctx)¶ Finalises the answer.
Last chance to affect what will get into the answer, including EDNS.
-
void *
data¶ The C module can store anything in here.
-
int
cb_slots[]¶ Internal to .
/daemon/ffimodule.c.
-
int (*
-
struct
kr_layer_pickle¶ - #include <layer.h>
Pickled layer state (api, input, state).
Public Members
-
struct kr_layer_pickle *
next¶
-
const struct kr_layer_api *
api¶
-
knot_pkt_t *
pkt¶
-
unsigned
state¶
-
struct kr_layer_pickle *
Utilities¶
Defines
-
kr_log_info¶
-
kr_log_error(...)¶
-
kr_log_deprecate(...)¶
-
kr_log_rtrace_enabled(req)¶ Return true if the query has request log handler installed.
-
kr_log_qtrace_enabled(qry)¶
-
VERBOSE_STATUS¶ Block run in verbose mode; optimized when not run.
-
WITH_VERBOSE(query)¶
-
kr_log_verbose¶
-
KR_DNAME_GET_STR(dname_str, dname)¶
-
KR_RRTYPE_GET_STR(rrtype_str, rrtype)¶
-
KR_RRKEY_LEN¶
-
SWAP(x, y)¶ Swap two places.
Note: the parameters need to be without side effects.
Typedefs
-
typedef void (*
trace_callback_f)(struct kr_request *request)¶ Callback for request events.
-
typedef void (*
trace_log_f)(const struct kr_request *request, const char *msg)¶ Callback for request logging handler.
- Parameters
[in] msg: Log message. Pointer is not valid after handler returns.
Functions
-
bool
kr_verbose_set(bool status)¶ Set verbose mode.
Not available if compiled with -DNOVERBOSELOG.
-
void
kr_log_req(const struct kr_request *const req, uint32_t qry_uid, const unsigned int indent, const char *source, const char *fmt, ...)¶ Log a message through the request log handler or stdout.
Caller is responsible for detecting verbose mode, use QRVERBOSE() macro.
- Parameters
qry_uid: query ID to append to request ID, 0 means “no query”indent: level of indentation between [req.qry][source] and messagesource: message sourcefmt: message format
-
void
kr_log_q(const struct kr_query *qry, const char *source, const char *fmt, ...)¶ Log a message through the request log handler or stdout.
Caller is responsible for detecting verbose mode, use QRVERBOSE() macro.
- Parameters
qry: current querysource: message sourcefmt: message format
-
int
strcmp_p(const void *p1, const void *p2)¶ A strcmp() variant directly usable for qsort() on an array of strings.
-
long
time_diff(struct timeval *begin, struct timeval *end)¶ Return time difference in miliseconds.
- Note
based on the _BSD_SOURCE timersub() macro
-
void
get_workdir(char *out, size_t len)¶ Get current working directory with fallback value.
-
char *
kr_strcatdup(unsigned n, ...)¶ Concatenate N strings.
-
char *
kr_absolutize_path(const char *dirname, const char *fname)¶ Construct absolute file path, without resolving symlinks.
- Return
malloc-ed string or NULL (+errno in that case)
-
void
kr_rnd_buffered(void *data, unsigned int size)¶ You probably want kr_rand_* convenience functions instead.
This is a buffered version of gnutls_rnd(GNUTLS_RND_NONCE, ..)
-
uint64_t
kr_rand_bytes(unsigned int size)¶ Return a few random bytes.
-
bool
kr_rand_coin(unsigned int nomin, unsigned int denomin)¶ Throw a pseudo-random coin, succeeding approximately with probability nomin/denomin.
low precision, only one byte of randomness (or none with extreme parameters)
tip: use !kr_rand_coin() to get the complementary probability
-
int
kr_memreserve(void *baton, void **mem, size_t elm_size, size_t want, size_t *have)¶ Memory reservation routine for knot_mm_t.
-
int
kr_pkt_recycle(knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶
-
int
kr_pkt_clear_payload(knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶
-
int
kr_pkt_put(knot_pkt_t *pkt, const knot_dname_t *name, uint32_t ttl, uint16_t rclass, uint16_t rtype, const uint8_t *rdata, uint16_t rdlen)¶ Construct and put record to packet.
-
void
kr_pkt_make_auth_header(knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶ Set packet header suitable for authoritative answer.
(for policy module)
-
const char *
kr_inaddr(const struct sockaddr *addr)¶ Address bytes for given family.
-
int
kr_inaddr_family(const struct sockaddr *addr)¶ Address family.
-
int
kr_inaddr_len(const struct sockaddr *addr)¶ Address length for given family, i.e.
sizeof(struct in*_addr).
-
int
kr_sockaddr_len(const struct sockaddr *addr)¶ Sockaddr length for given family, i.e.
sizeof(struct sockaddr_in*).
-
int
kr_sockaddr_cmp(const struct sockaddr *left, const struct sockaddr *right)¶ Compare two given sockaddr.
return 0 - addresses are equal, error code otherwise.
-
uint16_t
kr_inaddr_port(const struct sockaddr *addr)¶ Port.
-
void
kr_inaddr_set_port(struct sockaddr *addr, uint16_t port)¶ Set port.
-
int
kr_inaddr_str(const struct sockaddr *addr, char *buf, size_t *buflen)¶ Write string representation for given address as “<addr>#<port>”.
- Parameters
[in] addr: the raw address[out] buf: the buffer for output string[inout] buflen: the available(in) and utilized(out) length, including \0
-
int
kr_ntop_str(int family, const void *src, uint16_t port, char *buf, size_t *buflen)¶ Write string representation for given address as “<addr>#<port>”.
It’s the same as kr_inaddr_str(), but the input address is input in native format like for inet_ntop() (4 or 16 bytes) and port must be separate parameter.
-
char *
kr_straddr(const struct sockaddr *addr)¶
-
int
kr_straddr_family(const char *addr)¶ Return address type for string.
-
int
kr_family_len(int family)¶ Return address length in given family (struct in*_addr).
-
struct sockaddr *
kr_straddr_socket(const char *addr, int port, knot_mm_t *pool)¶ Create a sockaddr* from string+port representation.
Also accepts IPv6 link-local and AF_UNIX starting with “/” (ignoring port)
-
int
kr_straddr_subnet(void *dst, const char *addr)¶ Parse address and return subnet length (bits).
- Warning
’dst’ must be at least
sizeof(struct in6_addr)long.
-
int
kr_straddr_join(const char *addr, uint16_t port, char *buf, size_t *buflen)¶ Formats ip address and port in “addr#port” format.
and performs validation.
- Note
Port always formatted as five-character string with leading zeros.
- Return
kr_error(EINVAL) - addr or buf is NULL or buflen is 0 or addr doesn’t contain a valid ip address kr_error(ENOSP) - buflen is too small
-
int
kr_bitcmp(const char *a, const char *b, int bits)¶ Compare memory bitwise.
The semantics is “the same” as for memcmp(). The partial byte is considered with more-significant bits first, so this is e.g. suitable for comparing IP prefixes.
-
uint8_t
KEY_FLAG_RANK(const char *key)¶
-
bool
KEY_COVERING_RRSIG(const char *key)¶
-
int
kr_rrkey(char *key, uint16_t class, const knot_dname_t *owner, uint16_t type, uint16_t additional)¶ Create unique null-terminated string key for RR.
- Return
key length if successful or an error
- Parameters
key: Destination buffer for key size, MUST be KR_RRKEY_LEN or larger.class: RR class.owner: RR owner name.type: RR type.additional: flags (for instance can be used for storing covered type when RR type is RRSIG).
-
int
kr_ranked_rrarray_add(ranked_rr_array_t *array, const knot_rrset_t *rr, uint8_t rank, bool to_wire, uint32_t qry_uid, knot_mm_t *pool)¶ Add RRSet copy to a ranked RR array.
To convert to standard RRs inside, you need to call _finalize() afterwards, and the memory of rr->rrs.rdata has to remain until then.
- Return
array index (>= 0) or error code (< 0)
-
int
kr_ranked_rrarray_finalize(ranked_rr_array_t *array, uint32_t qry_uid, knot_mm_t *pool)¶ Finalize in_progress sets - all with matching qry_uid.
-
int
kr_ranked_rrarray_set_wire(ranked_rr_array_t *array, bool to_wire, uint32_t qry_uid, bool check_dups, bool (*extraCheck)(const ranked_rr_array_entry_t*))¶
-
char *
kr_pkt_text(const knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶ - Return
Newly allocated string representation of packet. Caller has to free() returned string.
-
char *
kr_rrset_text(const knot_rrset_t *rr)¶
-
char *
kr_dname_text(const knot_dname_t *name)¶
-
char *
kr_rrtype_text(const uint16_t rrtype)¶
-
char *
kr_module_call(struct kr_context *ctx, const char *module, const char *prop, const char *input)¶ Call module property.
-
uint16_t
kr_rrset_type_maysig(const knot_rrset_t *rr)¶ Return the (covered) type of an nonempty RRset.
-
uint64_t
kr_now()¶ The current time in monotonic milliseconds.
- Note
it may be outdated in case of long callbacks; see uv_now().
-
void
kr_uv_free_cb(uv_handle_t *handle)¶ Call free(handle->data); it’s useful e.g.
as a callback in uv_close().
-
int
knot_dname_lf2wire(knot_dname_t *dst, uint8_t len, const uint8_t *lf)¶ Convert name from lookup format to wire.
See knot_dname_lf
- Note
len bytes are read and len+1 are written with normal LF, but it’s also allowed that the final zero byte is omitted in LF.
- Return
the number of bytes written (>0) or error code (<0)
-
int
kr_dname_lf(uint8_t *dst, const knot_dname_t *src, bool add_wildcard)¶ Patched knot_dname_lf.
LF for “.” has length zero instead of one, for consistency. (TODO: consistency?)
- Note
packet is always NULL
- Parameters
add_wildcard: append the wildcard label
-
const char *
kr_strptime_diff(const char *format, const char *time1_str, const char *time0_str, double *diff)¶ Difference between two calendar times specified as strings.
- Parameters
[in] format: format for strptime[out] diff: result from C difftime(time1, time0)
-
void
kr_rrset_init(knot_rrset_t *rrset, knot_dname_t *owner, uint16_t type, uint16_t rclass, uint32_t ttl)¶
-
uint16_t
kr_pkt_has_dnssec(const knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶
-
uint16_t
kr_pkt_qclass(const knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶
-
uint16_t
kr_pkt_qtype(const knot_pkt_t *pkt)¶
-
uint32_t
kr_rrsig_sig_inception(const knot_rdata_t *rdata)¶
-
uint32_t
kr_rrsig_sig_expiration(const knot_rdata_t *rdata)¶
-
uint16_t
kr_rrsig_type_covered(const knot_rdata_t *rdata)¶
-
time_t
kr_file_mtime(const char *fname)¶
-
long long
kr_fssize(const char *path)¶ Return filesystem size in bytes.
Variables
-
bool
kr_verbose_status¶ Whether in verbose mode.
Only use this for reading.
-
const uint8_t
KEY_FLAG_RRSIG= 0x02¶
-
union
inaddr¶ - #include <utils.h>
Simple storage for IPx address or AF_UNSPEC.
Functions
-
int
kr_error(int x)¶
Generics library¶
This small collection of “generics” was born out of frustration that I couldn’t find no such thing for C. It’s either bloated, has poor interface, null-checking is absent or doesn’t allow custom allocation scheme. BSD-licensed (or compatible) code is allowed here, as long as it comes with a test case in tests/test_generics.c.
array - a set of simple macros to make working with dynamic arrays easier.
queue - a FIFO + LIFO queue.
map - a Crit-bit tree key-value map implementation (public domain) that comes with tests.
set - set abstraction implemented on top of
map(unused now).pack - length-prefixed list of objects (i.e. array-list).
lru - LRU-like hash table
trie - a trie-based key-value map, taken from knot-dns
array¶
A set of simple macros to make working with dynamic arrays easier.
MIN(array_push(arr, val), other)
- Note
The C has no generics, so it is implemented mostly using macros. Be aware of that, as direct usage of the macros in the evaluating macros may lead to different expectations:
May evaluate the code twice, leading to unexpected behaviour. This is a price to pay for the absence of proper generics.
Example usage:
array_t(const char*) arr;
array_init(arr);
// Reserve memory in advance
if (array_reserve(arr, 2) < 0) {
return ENOMEM;
}
// Already reserved, cannot fail
array_push(arr, "princess");
array_push(arr, "leia");
// Not reserved, may fail
if (array_push(arr, "han") < 0) {
return ENOMEM;
}
// It does not hide what it really is
for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.len; ++i) {
printf("%s\n", arr.at[i]);
}
// Random delete
array_del(arr, 0);
Defines
-
array_t(type)¶ Declare an array structure.
-
array_init(array)¶ Zero-initialize the array.
-
array_clear(array)¶ Free and zero-initialize the array (plain malloc/free).
-
array_clear_mm(array, free, baton)¶ Make the array empty and free pointed-to memory.
Mempool usage: pass mm_free and a knot_mm_t* .
-
array_reserve(array, n)¶ Reserve capacity for at least n elements.
- Return
0 if success, <0 on failure
-
array_reserve_mm(array, n, reserve, baton)¶ Reserve capacity for at least n elements.
Mempool usage: pass kr_memreserve and a knot_mm_t* .
- Return
0 if success, <0 on failure
-
array_push_mm(array, val, reserve, baton)¶ Push value at the end of the array, resize it if necessary.
Mempool usage: pass kr_memreserve and a knot_mm_t* .
- Note
May fail if the capacity is not reserved.
- Return
element index on success, <0 on failure
-
array_push(array, val)¶ Push value at the end of the array, resize it if necessary (plain malloc/free).
- Note
May fail if the capacity is not reserved.
- Return
element index on success, <0 on failure
-
array_pop(array)¶ Pop value from the end of the array.
-
array_del(array, i)¶ Remove value at given index.
- Return
0 on success, <0 on failure
-
array_tail(array)¶ Return last element of the array.
- Warning
Undefined if the array is empty.
queue¶
A queue, usable for FIFO and LIFO simultaneously.
Both the head and tail of the queue can be accessed and pushed to, but only the head can be popped from.
Example usage:
// define new queue type, and init a new queue instance
typedef queue_t(int) queue_int_t;
queue_int_t q;
queue_init(q);
// do some operations
queue_push(q, 1);
queue_push(q, 2);
queue_push(q, 3);
queue_push(q, 4);
queue_pop(q);
assert(queue_head(q) == 2);
assert(queue_tail(q) == 4);
// you may iterate
typedef queue_it_t(int) queue_it_int_t;
for (queue_it_int_t it = queue_it_begin(q); !queue_it_finished(it);
queue_it_next(it)) {
++queue_it_val(it);
}
assert(queue_tail(q) == 5);
queue_push_head(q, 0);
++queue_tail(q);
assert(queue_tail(q) == 6);
// free it up
queue_deinit(q);
// you may use dynamic allocation for the type itself
queue_int_t *qm = malloc(sizeof(queue_int_t));
queue_init(*qm);
queue_deinit(*qm);
free(qm);
- Note
The implementation uses a singly linked list of blocks (“chunks”) where each block stores an array of values (for better efficiency).
Defines
-
queue_t(type)¶ The type for queue, parametrized by value type.
-
queue_init(q)¶ Initialize a queue.
You can malloc() it the usual way.
-
queue_deinit(q)¶ De-initialize a queue: make it invalid and free any inner allocations.
-
queue_push(q, data)¶ Push data to queue’s tail.
(Type-safe version; use _impl() otherwise.)
-
queue_push_head(q, data)¶ Push data to queue’s head.
(Type-safe version; use _impl() otherwise.)
-
queue_pop(q)¶ Remove the element at the head.
The queue must not be empty.
-
queue_head(q)¶ Return a “reference” to the element at the head (it’s an L-value).
The queue must not be empty.
-
queue_tail(q)¶ Return a “reference” to the element at the tail (it’s an L-value).
The queue must not be empty.
-
queue_len(q)¶ Return the number of elements in the queue (very efficient).
-
queue_it_t(type)¶ Type for queue iterator, parametrized by value type.
It’s a simple structure that owns no other resources. You may NOT use it after doing any push or pop (without _begin again).
-
queue_it_begin(q)¶ Initialize a queue iterator at the head of the queue.
If you use this in assignment (instead of initialization), you will unfortunately need to add corresponding type-cast in front. Beware: there’s no type-check between queue and iterator!
-
queue_it_val(it)¶ Return a “reference” to the current element (it’s an L-value) .
-
queue_it_finished(it)¶ Test if the iterator has gone past the last element.
If it has, you may not use _val or _next.
-
queue_it_next(it)¶ Advance the iterator to the next element.
map¶
A Crit-bit tree key-value map implementation.
Example usage:
- Warning
If the user provides a custom allocator, it must return addresses aligned to 2B boundary.
map_t map = map_make(NULL);
// Custom allocator (optional)
map.malloc = &mymalloc;
map.baton = &mymalloc_context;
// Insert k-v pairs
int values = { 42, 53, 64 };
if (map_set(&map, "princess", &values[0]) != 0 ||
map_set(&map, "prince", &values[1]) != 0 ||
map_set(&map, "leia", &values[2]) != 0) {
fail();
}
// Test membership
if (map_contains(&map, "leia")) {
success();
}
// Prefix search
int i = 0;
int count(const char *k, void *v, void *ext) { (*(int *)ext)++; return 0; }
if (map_walk_prefixed(map, "princ", count, &i) == 0) {
printf("%d matches\n", i);
}
// Delete
if (map_del(&map, "badkey") != 0) {
fail(); // No such key
}
// Clear the map
map_clear(&map);
Defines
-
map_walk(map, callback, baton)¶
Functions
-
void *
map_get(map_t *map, const char *str)¶ Returns value if map contains str.
Note: NULL may mean two different things.
-
int
map_set(map_t *map, const char *str, void *val)¶ Inserts str into map.
Returns 0 if new, 1 if replaced, or ENOMEM.
-
int
map_walk_prefixed(map_t *map, const char *prefix, int (*callback)(const char*, void*, void*), void *baton, )¶ Calls callback for all strings in map with the given prefix.
Returns value immediately if a callback returns nonzero.
- Parameters
map:prefix: required string prefix (empty => all strings)callback: callback parameters are (key, value, baton)baton: passed uservalue
-
struct
map_t¶ - #include <map.h>
Main data structure.
set¶
A set abstraction implemented on top of map.
Example usage:
- Note
The API is based on map.h, see it for more examples.
set_t set = set_make(NULL);
// Insert keys
if (set_add(&set, "princess") != 0 ||
set_add(&set, "prince") != 0 ||
set_add(&set, "leia") != 0) {
fail();
}
// Test membership
if (set_contains(&set, "leia")) {
success();
}
// Prefix search
int i = 0;
int count(const char *s, void *n) { (*(int *)n)++; return 0; }
if (set_walk_prefixed(set, "princ", count, &i) == 0) {
printf("%d matches\n", i);
}
// Delete
if (set_del(&set, "badkey") != 0) {
fail(); // No such key
}
// Clear the set
set_clear(&set);
Defines
-
set_make¶ Creates an new, empty critbit set
-
set_contains(set, str)¶ Returns non-zero if set contains str
-
set_add(set, str)¶ Inserts str into set. Returns 0 if new, 1 if already present, or ENOMEM.
-
set_del(set, str)¶ Deletes str from the set, returns 0 on suceess
-
set_clear(set)¶ Clears the given set
-
set_walk(set, callback, baton)¶ Calls callback for all strings in map
-
set_walk_prefixed(set, prefix, callback, baton)¶ Calls callback for all strings in set with the given prefix
pack¶
A length-prefixed list of objects, also an array list.
Each object is prefixed by item length, unlike array this structure permits variable-length data. It is also equivallent to forward-only list backed by an array.
- Note
Maximum object size is 2^16 bytes, see pack_objlen_t
Example usage:
pack_t pack;
pack_init(pack);
// Reserve 2 objects, 6 bytes total
pack_reserve(pack, 2, 4 + 2);
// Push 2 objects
pack_obj_push(pack, U8("jedi"), 4)
pack_obj_push(pack, U8("\xbe\xef"), 2);
// Iterate length-value pairs
uint8_t *it = pack_head(pack);
while (it != pack_tail(pack)) {
uint8_t *val = pack_obj_val(it);
it = pack_obj_next(it);
}
// Remove object
pack_obj_del(pack, U8("jedi"), 4);
pack_clear(pack);
Defines
-
pack_init(pack)¶ Zero-initialize the pack.
-
pack_clear(pack)¶ Make the pack empty and free pointed-to memory (plain malloc/free).
-
pack_clear_mm(pack, free, baton)¶ Make the pack empty and free pointed-to memory.
Mempool usage: pass mm_free and a knot_mm_t* .
-
pack_reserve(pack, objs_count, objs_len)¶ Reserve space for additional objects in the pack (plain malloc/free).
- Return
0 if success, <0 on failure
-
pack_reserve_mm(pack, objs_count, objs_len, reserve, baton)¶ Reserve space for additional objects in the pack.
Mempool usage: pass kr_memreserve and a knot_mm_t* .
- Return
0 if success, <0 on failure
-
pack_head(pack)¶ Return pointer to first packed object.
Recommended way to iterate: for (uint8_t *it = pack_head(pack); it != pack_tail(pack); it = pack_obj_next(it))
-
pack_tail(pack)¶ Return pack end pointer.
Typedefs
-
typedef uint16_t
pack_objlen_t¶ Packed object length type.
-
typedef see_source_code
pack_t¶ Pack is defined as an array of bytes.
Functions
-
pack_objlen_t
pack_obj_len(uint8_t *it)¶ Return packed object length.
-
uint8_t *
pack_obj_val(uint8_t *it)¶ Return packed object value.
-
uint8_t *
pack_obj_next(uint8_t *it)¶ Return pointer to next packed object.
-
int
pack_obj_push(pack_t *pack, const uint8_t *obj, pack_objlen_t len)¶ Push object to the end of the pack.
- Return
0 on success, negative number on failure
-
uint8_t *
pack_obj_find(pack_t *pack, const uint8_t *obj, pack_objlen_t len)¶ Returns a pointer to packed object.
- Return
pointer to packed object or NULL
-
int
pack_obj_del(pack_t *pack, const uint8_t *obj, pack_objlen_t len)¶ Delete object from the pack.
- Return
0 on success, negative number on failure
lru¶
A lossy cache.
Example usage:
// Define new LRU type
typedef lru_t(int) lru_int_t;
// Create LRU
lru_int_t *lru;
lru_create(&lru, 5, NULL, NULL);
// Insert some values
int *pi = lru_get_new(lru, "luke", strlen("luke"), NULL);
if (pi)
*pi = 42;
pi = lru_get_new(lru, "leia", strlen("leia"), NULL);
if (pi)
*pi = 24;
// Retrieve values
int *ret = lru_get_try(lru, "luke", strlen("luke"), NULL);
if (!ret) printf("luke dropped out!\n");
else printf("luke's number is %d\n", *ret);
char *enemies[] = {"goro", "raiden", "subzero", "scorpion"};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int *val = lru_get_new(lru, enemies[i], strlen(enemies[i]), NULL);
if (val)
*val = i;
}
// We're done
lru_free(lru);
- Note
The implementation tries to keep frequent keys and avoid others, even if “used recently”, so it may refuse to store it on lru_get_new(). It uses hashing to split the problem pseudo-randomly into smaller groups, and within each it tries to approximate relative usage counts of several most frequent keys/hashes. This tracking is done for more keys than those that are actually stored.
Defines
-
lru_t(type)¶ The type for LRU, parametrized by value type.
-
lru_create(ptable, max_slots, mm_ctx_array, mm_ctx)¶ Allocate and initialize an LRU with default associativity.
The real limit on the number of slots can be a bit larger but less than double.
- Note
The pointers to memory contexts need to remain valid during the whole life of the structure (or be NULL).
- Parameters
ptable: pointer to a pointer to the LRUmax_slots: number of slotsmm_ctx_array: memory context to use for the huge array, NULL for default If you pass your own, it needs to produce CACHE_ALIGNED allocations (ubsan).mm_ctx: memory context to use for individual key-value pairs, NULL for default
-
lru_free(table)¶ Free an LRU created by lru_create (it can be NULL).
-
lru_reset(table)¶ Reset an LRU to the empty state (but preserve any settings).
-
lru_get_try(table, key_, len_)¶ Find key in the LRU and return pointer to the corresponding value.
- Return
pointer to data or NULL if not found
- Parameters
table: pointer to LRUkey_: lookup keylen_: key length
-
lru_get_new(table, key_, len_, is_new)¶ Return pointer to value, inserting if needed (zeroed).
- Return
pointer to data or NULL (can be even if memory could be allocated!)
- Parameters
table: pointer to LRUkey_: lookup keylen_: key lengthkeysis_new: pointer to bool to store result of operation (true if entry is newly added, false otherwise; can be NULL).
-
lru_apply(table, function, baton)¶ Apply a function to every item in LRU.
- Parameters
table: pointer to LRUfunction: enum lru_apply_do (*function)(const char *key, uint len, val_type *val, void *baton) See enum lru_apply_do for the return type meanings.baton: extra pointer passed to each function invocation
-
lru_capacity(table)¶ Return the real capacity - maximum number of keys holdable within.
- Parameters
table: pointer to LRU
trie¶
Typedefs
-
typedef void *
trie_val_t¶ Native API of QP-tries:
keys are char strings, not necessarily zero-terminated, the structure copies the contents of the passed keys
values are void* pointers, typically you get an ephemeral pointer to it
key lengths are limited by 2^32-1 ATM
XXX EDITORS: trie.{h,c} are synced from https://gitlab.nic.cz/knot/knot-dns/tree/68352fc969/src/contrib/qp-trie only with tiny adjustments, mostly include lines and KR_EXPORT.
Element value.
-
typedef struct trie
trie_t¶ Opaque structure holding a QP-trie.
-
typedef struct trie_it
trie_it_t¶ Opaque type for holding a QP-trie iterator.
Functions
-
trie_val_t *
trie_get_try(trie_t *tbl, const char *key, uint32_t len)¶ Search the trie, returning NULL on failure.
-
trie_val_t *
trie_get_first(trie_t *tbl, char **key, uint32_t *len)¶ Return pointer to the minimum. Optionally with key and its length.
-
trie_val_t *
trie_get_ins(trie_t *tbl, const char *key, uint32_t len)¶ Search the trie, inserting NULL trie_val_t on failure.
-
int
trie_get_leq(trie_t *tbl, const char *key, uint32_t len, trie_val_t **val)¶ Search for less-or-equal element.
- Return
KNOT_EOK for exact match, 1 for previous, KNOT_ENOENT for not-found, or KNOT_E*.
- Parameters
tbl: Trie.key: Searched key.len: Key length.val: Must be valid; it will be set to NULL if not found or errored.
-
int
trie_apply(trie_t *tbl, int (*f)(trie_val_t*, void*), void *d, )¶ Apply a function to every trie_val_t, in order.
- Return
First nonzero from f() or zero (i.e. KNOT_EOK).
- Parameters
d: Parameter passed as the second argument to f().
-
int
trie_del(trie_t *tbl, const char *key, uint32_t len, trie_val_t *val)¶ Remove an item, returning KNOT_EOK if succeeded or KNOT_ENOENT if not found.
If val!=NULL and deletion succeeded, the deleted value is set.
-
int
trie_del_first(trie_t *tbl, char *key, uint32_t *len, trie_val_t *val)¶ Remove the first item, returning KNOT_EOK on success.
You may optionally get the key and/or value. The key is copied, so you need to pass sufficient len, otherwise kr_error(ENOSPC) is returned.
-
trie_it_t *
trie_it_begin(trie_t *tbl)¶ Create a new iterator pointing to the first element (if any).
-
void
trie_it_next(trie_it_t *it)¶ Advance the iterator to the next element.
Iteration is in ascending lexicographical order. In particular, the empty string would be considered as the very first.
- Note
You may not use this function if the trie’s key-set has been modified during the lifetime of the iterator (modifying values only is OK).
-
const char *
trie_it_key(trie_it_t *it, size_t *len)¶ Return pointer to the key of the current element.
- Note
The optional len is uint32_t internally but size_t is better for our usage, as it is without an additional type conversion.
-
trie_val_t *
trie_it_val(trie_it_t *it)¶ Return pointer to the value of the current element (writable).